I am teaching an Exadata class this week. One of the questions that does come often in the class is to explain different network types available in Exadata. So here they are.
Admin Network
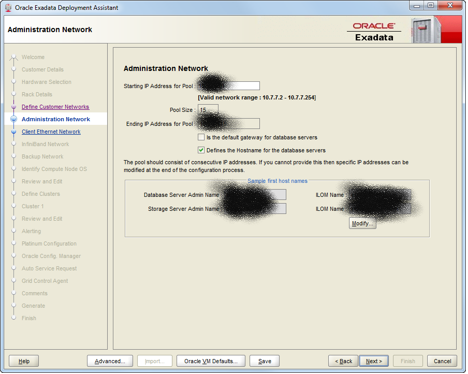
Admin network was earlier called Management work. This is used basically to manage all the compute nodes, cell nodes and also pretty much all the other manageable components (physical) of the box. Why it’s an important network configuration cos using this, via SSH, you will manage all of these components from your organization’s network. Since this network is required to be available from the outside, it’s available from the supplied Cisco switch within the Exadata box.
As you can see, the wizard from Oracle Exadata Deployment Assistant(OEDA) tool will ask you to enter the starting IP in the tool. Pool is going to be the number of IPs needed which is based on the given configuration of the box. In this example, it’s a Quarter Rack and that’s why 15 IP addresses are required. Ending IP address will be the last IP address in the same range of the first IP address entered by you. Next option is supposed to be selected if you want to use this admin network as a path for your database servers. Define Hostnames is to mention the database server’s names in the admin network.
Client Network
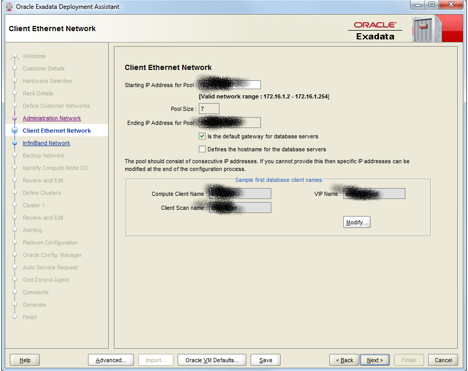
Next is the Client network which is fairly simple. This is going to be the network that’s used by the users to access the database. So obviously, it’s going to network details through which the database servers can be accessed by the clients/users. So here the number of IP addresses are based on the number of database nodes that you have in your box(multiplied by 2 because of bonding) and 3 addresses for the SCAN. Since we are using a QR here, so there are 2 db nodes. Thus 2 db nodes * 2 plus 3 SCAN addresses are resulting into the required 7 IP addresses. As mentioned, this is the default and preferred way that the database servers are going to be access through. If you want to mention the hostnames for your database nodes, you can do so by selecting the checkbox. Other details are simple I believe.
Infiniband Network
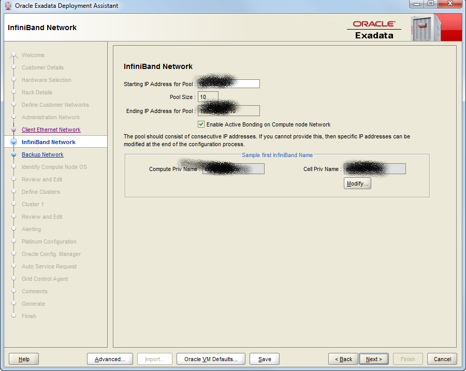
Infiniband(IB) network works within the Exadata database machine to connect the db nodes with the cell nodes. Since this is going to be available for just within the machine, it must be configured on a network configuration that’s not used by the clients. Depending on your Exadata version, the bonded network interface can be used in Active-Passive or Active-Active manner. IB is used by both db nodes and storage nodes. So the number of IP addresses required are going to be based on the number of both types of nodes in your configuration. For a QR, since there are 2 db nodes and 3 cell nodes, including bonding, there is going to be 10(5*2) IP addresses required.
Backup Network
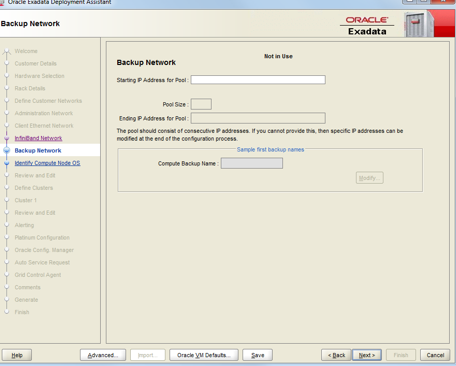
This is an optional network. Unless you don’t need to configure a standby, or a tape backup using a remote system or any of such thing, this network remains unused.
So these are the networks that are available in Exadata. Hope this post helps in clarifying the types a little better.
Aman….


Recent Comments